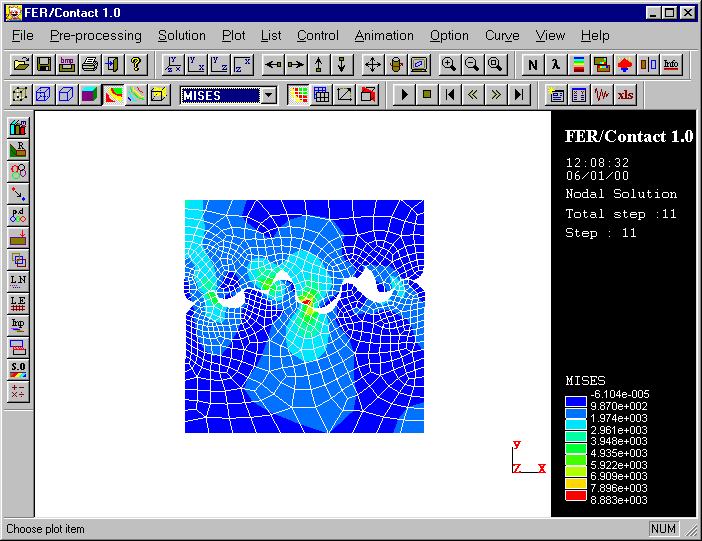
FER/Contact 1.0
FER/Contact is a complete package devoted to the modelling of frictional
contact problems. The pre/postprocessor and the solver are developed using C++
Object Oriented Programming, MFC and OpenGL graphical tools on the platform
Windows 98/NT.
The code FER/Contact is capable of handling a wide range of
engineering applications. These include situations in which:
- the contact occurs between two or more deformable bodies
or between deformable bodies and rigid bodies in two or three dimension
problems, the constitutive law of deformable bodies being linear or non
linear with large deformations and large displacements;
- the contact may be sticking or sliding, with or without
Coulomb friction;
- the repeated "contact<->non contact" and
"sticking<->sliding" are permitted;
- the relative displacement between contact bodies can be
large;
- the contact surface can have small curvature radius, and
even sharp corners.
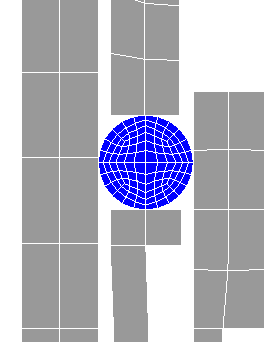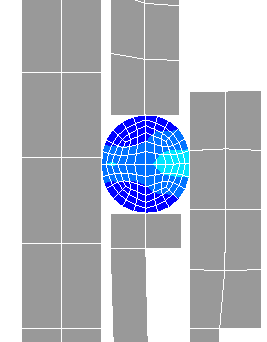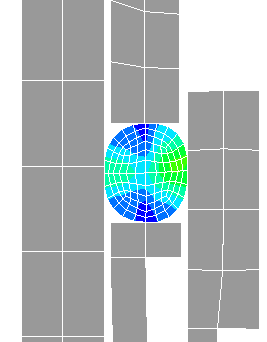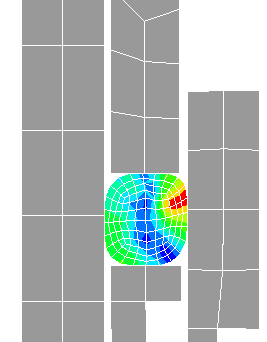
The bipotential method proposed by De Saxcé and Feng
has be used to deal with the contact problem with Coulomb's friction in this
software. Some characteristics of the bipotential method:
- the unilateral contact and the friction are coupled via
a contact bipotential. This variational approach is more efficient and
simpler than the classic one that involves two variational principles and
two inequalities utilized respectively for unilateral contact and
friction.
- the semi-analytical formula has been developed so that
the contact reactions can be obtained accurately and contact Signorini's
conditions and friction laws are satisfied.
- the frictional contact problem is treated in a reduced
system and the global finite element stiffness matrix is not changed as
opposite to the penalty method or to the Lagrangian multiplier method. This
makes it easy to implement the contact and friction calculation in existing
finite element software.
- the method neither augments the degrees of freedom nor
changes the global stiffness matrix. It is especially suitable for the
solution of a large system.